With our expertise in air quality management and dispersion modelling, we can give you access to the tools and data you need for your air quality assessment work and the training to use them. We also offer consultancy services performed by our experts.
Advantages of dispersion modelling
We have a range of systems and tools for use on all spatial scales in air quality assessment, community planning or emergency preparedness.
Our modelling systems give:
- An overview of the problem through geographically distributed results.
- Information on source apportionment.
What emission sector contributes where and to what extent? - Deeper understanding of the problem.
When and why do concentration peaks occur? What is the effect of the chemical interaction between pollutants? - Synergy with measurements.
How do measurements and model results compare? Is the measuring location fit for purpose? - Ability to perform scenario studies.
What is the most efficient emission reduction measure?
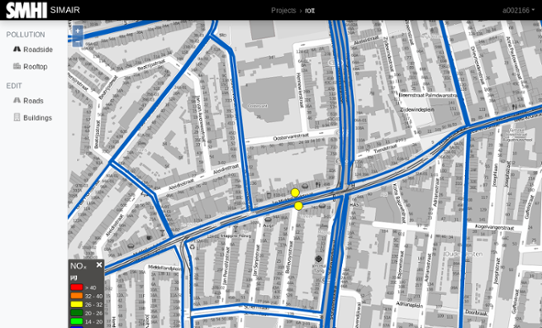
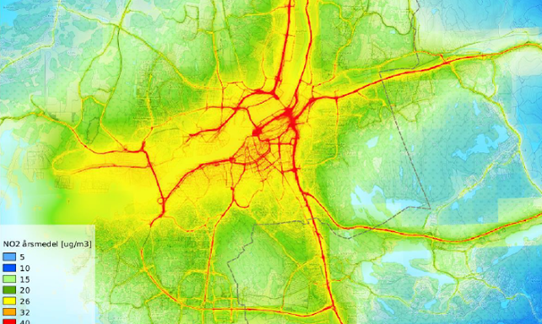
The SIMAIR system for urban modelling
SIMAIR is an easy-to-use tool for municipalities/cities and decision makers on local and urban scales. As a user you can evaluate the impact from the most critical sectors such as roads, heating and industries and study what effect local emission reduction measures would have on the air quality.
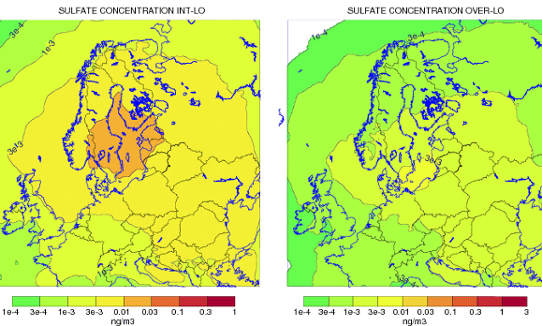
The MATCH model for regional modelling
For problems on larger scales than single cities, we use the powerful MATCH model. It can be used to study the nation-wide consequences of air pollution on topics such as health issues, damage on crops, effects from volcanic eruptions, nuclear power plant accidents and long-range transported contributions.